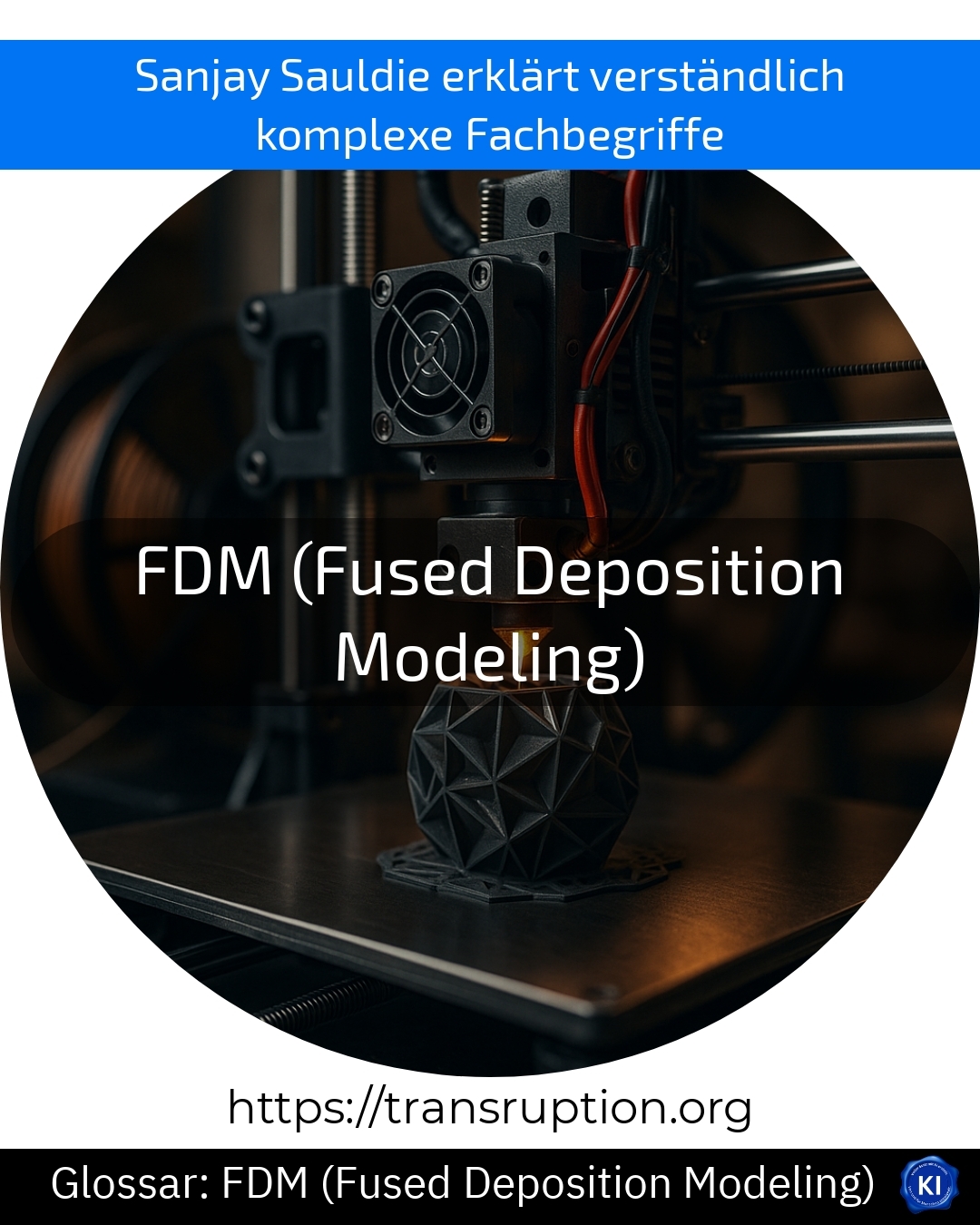
FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) is a key technology in the field of 3D printing, Industry and Factory 4.0 as well as Sustainability and Environment 4.0. FDM means "fused deposition modelling" and is the most widely used method for 3D printing of plastic parts.
The process works like this: a heated nozzle melts plastic filament and applies it layer by layer to a building platform. This creates a three-dimensional object piece by piece - similar to a hot glue gun, only much more precise and computer-controlled. Once one layer has dried, the next follows until the entire component is finished.
An illustrative example: a company needs special brackets for devices that it cannot buy off the shelf. With FDM, a customised component can be produced in-house within a few hours - quickly, cost-effectively and without a lot of material waste.
FDM therefore offers a flexible and sustainable way of producing prototypes, spare parts or small batches directly on site without major investment. This facilitates innovation and significantly shortens the time from the idea to the finished product.